Summary
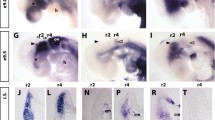
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) promotes the development of primary neural crest cells grown in tissue culture to the sympathoadrenal (SA) lineage. Independent studies have characterized the expression patterns of SA-lineage genes in developing chicken embryo; however, studies using cultured primary neural crest cells have characterized only the expression patterns of the catecholaminergic markers, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and catecholamines (CAs). To further explore the molecular mechanisms that control SA-cell development using the in vitro model system, it is crucial to define the expression patterns of both the catecholaminergic markers and the genes regulating SA-lineage determination. Accordingly, we defined, in the absence and presence of BMP-2, the temporal expression patterns of TH and CA, the SA lineage-determining genes ASH-1, Phox2a, and Phox2b, the GATA-2 gene, and the pan-neuronal SCG10 gene. Comparison of these data with the reported temporal and spatial patterns of expression in vivo demonstrate that the inductive steps of SA-lineage determination, including the specification of neurotransmitter identity and neuronal fate, are recapitulated in the neural-crest culture system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. J. Molecular control of cell fate in the neural crest: the sympathoadrenal lineage. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 16:129–158; 1993.
Anderson, D. J.;Cellular and molecular biology of neural crest cell lineage determination. Trends Genet. 13:276–280; 1997.
Anderson, D. J.; Axel, R. Molecular probes for the development and plasticity of neural crest derivatives. Cell 42:649–662; 1985.
Bilodeau, M. L.; Boulineau, T.; Hullinger, R. L.; Andrisani, O. A. Cyclic AMP signaling functions as a bi-modal switch on sympathoadrenal cell development in cultured neural crest cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:3004–3014; 2000.
Briegel, K.; Kim, K. C.; Plank, C.; Beug, H.; Engel, J. D.; Zenke, M. Ectopic expression of a conditional GATA-2/estrogen receptor chimera arrests erythroid differentiation in a hormone-dependent manner. Genes Dev. 7:1097–1109; 1993.
Cahn, R. D.; Coon, H. G.; Cahn, M. B. Cell culture and cloning techniques. In: Wilt, F. H.; Wessels, N. K., ed. Methods in developmental biology. New York: Thomas Y. Crowell Company; 1967;493–530.
Christie, D. S.; Forbes, M. E.; Maxwell, G. D. Phenotypic properties of catecholamine-positive cells that differentiate in avian neural crest cultures. J. Neurosci. 7:3749–3763; 1987.
Durbec, P. L.; Larsson-Blomberg, L. B.; Schuchardt, A.; Costantini, F.; Pachnis, V. Common origin and developmental dependence on c-ret of subsets of enteric and sympathetic neuroblasts. Development 122:349–358; 1996.
Enemar, A.; Falck, B.; Hakanson, R. Observations on the appearance of norepinephrine in the sympathetic nervous system of the chick embryo. Dev. Biol. 11:268–283; 1965.
Ernsberger, U.; Patzke, H.; Tissier-Seta, J. P.; Reh, T.; Goridis, C.; Rohrer, H. The expression of tyrosine hydroxylase and the transcription factors cPhox-2 and Cash-1: evidence for distinct inductive steps in the differentiation of chick sympathetic precursor cells. Mech. Dev. 52:125–136; 1995.
Fauquet, M.; Ziller, C. A monoclonal antibody directed against quail tyrosine hydroxylase: description and use in immunocytochemical studies on differentiating neural crest cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37:1197–1205; 1989.
Furness, J. B.; Costa, M.; Wilson, A. J. Water-stable fluorophores, produced by reaction with aldehyde solutions, for the histochemical localization of catechol- and indolethylamines. Histochemistry 52:159–170; 1977.
Goridis, C.; Brunet, J.-F. Transcriptional control of neurotransmitter phenotype. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9:47–53; 1999.
Croves, A. K.; Anderson, D. J. Role of environmental signals and transcriptional regulators in neural crest development. Dev. Genet. 18:64–72; 1996.
Groves, A. K.; George, K. M.; Tissier-Seta, J. P.; Engel, J. D.; Brunet, J. F.; Anderson, D. J. Differential regulation of transcription factor gene expression and phenotypic markers in developing sympathetic neurons. Development 121:887–901; 1995.
Guillemot, F.; Lo, L. C.; Johnson, J. E.; Auerbach, A.; Anderson, D. J.; Joyner, A. L. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell 75:463–476; 1993.
Hamburger, V.; Hamilton, H. L. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. Dev. Dyn. 195:231–272; 1992.
Hirsch, M. R.; Tiveron, M. C.; Guillemot, F.; Brunet, J. F.; Goridis, C.: Control of noradrenergic differentiation and Phox2a expression by MASH1 in the central and peripheral nervous system. Development 125:599–608; 1998.
Johnson, J. E.; Birren, S. J.; Anderson, D. J. Two rat homologues of Drosophila achaete-scute specifically expressed in neuronal precursors. Nature 346:858–861; 1990.
Kirby, M. L.; Gilmore, S. A. A correlative histofluorescence and light microscopic study of the formation of the sympathetic trunks in chick embryos. Anat. Rec. 186:437–449; 1976.
Lo, L. C.; Johnson, J. E.; Wuenschell, C. W.; Saito, T.; Anderson, D. J. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is transiently expressed by spatially restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev. 5:1524–1537; 1991.
Lo, L.; Morin, X.; Brunet, J. F.; Anderson, D. J. Specification of neurotransmitter identity by Phox2 proteins in neural crest stem cells. Neuron 22:693–705; 1999.
Lo, L.; Sommer, L.; Anderson, D. J. MASH1 maintains competence for BMP2-induced neuronal differentiation in post-migratory neural crest cells. Curr. Biol. 7:440–450; 1997.
Lo, L.; Tiveron, M. C.; Anderson, D. J. MASH1 activates expression of the paired homeodomain transcription factor Phox2a, and couples panneuronal and subtype-specific components of autonomic neuronal identity. Development 125:609–620; 1998.
Mains, R. E.; Patterson, P. H. Primary cultures of dissociated sympathetic neurons. I. Establishment of long-term growth in culture and studies of differentiated properties. J. Cell. Biol. 59:329–345; 1973.
Maxwell, G. D.; Sietz, P. D.; Rafford, C. E. Synthesis and accumulation of putative neurotransmitters by cultured neural crest cells. J. Neurosci. 2:879–888; 1982.
Morin, X.; Cremer, H.; Hirsch, M. R.; Kapur, R. P.; Goridis, C.; Brunet J. F. Defects in sensory and autonomic ganglia and absence of locus coeruleus in mice deficient for the homeobox gene Phox2a. Neuron 18:411–423; 1997.
Newgreen, D. F.; Allan, I. J.; Young, H. M.; Southwell, B. R. Accumulation of exogenous catecholamines in the neural tube and non-neural tissues of the early fowl embryo: correlation with morphogenetic movements. Wilhelm Roux's Arch. 190:320–330; 1981.
Pattyn, A.; Morin, X.; Cremer, H.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J. F. Expression and interactions of the two closely related homeobox genes Phox2a and Phox2b during neurogenesis. Development 124:4065–4075; 1997.
Pattyn, A.; Morin, X.; Cremer, H.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J. F. The homeobox gene Phox2b is essential for the development of autonomic neural creast derivatives. Nature 399:366–370; 1999.
Ramain, P.; Heitzler, P.; Haenlin, M.; Simpson, P. Pannier, a negative regulator of achaete and scute in Drosophila, encodes a zinc finger protein with homology to the vertebrate transcription factor GATA-1. Development 119:1277–1291; 1993.
Reissmann, E.; Ernsberger, U.; Francis-West, P. H.; Rueger, D.; Brickell, P. M.; Rohrer, H. Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein-4 and bone morphogenetic protein-7 in the differentiation of the adrenergic phenotype in developing sympathetic neurons. Development 122:2079–2088; 1996.
Shah, N. M.; Groves, A. K.; Anderson, D. J. Alternative neural crest cell fates are instructively promoted by TGFbeta superfamily members. Cell 85:331–343; 1996.
Sommer, L.; Shah, N.; Rao, M.; Anderson, D. J. The cellular function of MASH1 in autonomic neurogenesis. Neuron 15:1245–1258; 1995.
Stanke, M.; Junghans, D.; Geissen, M.; Goridis, C.; Ernsberger, U.; Rohrer, H. The Phox2 homeodomain proteins are sufficient to promote the development of sympathetic neurons. Development 126:4087–4094; 1999.
Stein, R.; Mori, N.; Matthews, K.; Lo, L. C.; Anderson, D. J. The NGF-inducible SCG10 mRNA encodes a novel membrane-bound protein present in growth cones and abundant in developing neurons. Neuron 1:463–476; 1988.
Swanson, D. J.; Zellmer, E.; Lewis, E. J. The homeodomain protein Arix interacts synergistically with cyclic AMP to regulate expression of neurotransmitter biosynthetic genes. J. Biol. Chem. 272:27,382–27,392; 1997.
Tsai, F. Y.; Keller, G.; Kuo, F. C.; Weiss, M.; Chen, J.; Rosenblatt, M.; Alt, F. W.; Orkin, S. H. An early haematopoietic defect in mice lacking the transcription factor GATA-2. Nature 371:221–226; 1994.
Valarche, I.; Tissier-Seta, J. P.; Hirsch, M. R.; Martinez, S.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J. F. The mouse homeodomain protein Phox2 regulates Ncam promoter activity in concert with Cux/CDP and is a putative determinant of neurotransmitter phenotype. Development 119:881–896; 1993.
Varley, J. E.; Maxwell, G. D. BMP-2 and BMP-4, but not BMP-6, increase the number of adrenergic cells which develop in quail trunk neural crest cultures. Exp. Neurol. 140:84–94; 1996.
Varley, J. E.; McPherson, C. E.; Zou, H., Niswander, L.; Maxwell, G. D. Expression of a constitutively active type I BMP receptor using a retroviral vector promotes the development of adrenergic cells in neural crest cultures. Dev. Biol. 196:107–118; 1998.
Varley, J. E.; Wehby, R. G.; Rueger, D. C.; Maxwell, G. D. Number of adrenergic and islet-1 immunoreactive cells is increased in avian trunk neural crest cultures in the presence of human recombinant osteogenic protein-1. Dev. Dyn. 203:434–447; 1995.
Yamamoto, M.; Ko, L. J.; Leonard, M. W.; Beug, H.; Orkin, S. H.; Engel, J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 4:1650–1662; 1990.
Yang, C.; Kim, H. S.; Seo, H.; Kim, C. H.; Brunet, J. F.; Kim, K. S. Paired-like homeodomain proteins, Phox2a and Phox2b, are responsible for noradrenergic cell-specific transcription of the dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene. J. Neurochem. 71:1813–1826; 1998.
Zellmer, E.; Zhang, Z.; Greco, D.; Rhodes, J.; Cassel, S.; Lewis, E. J. A homeodomain protein selectively expressed in noradrenergic tissue regulates transcription of neurotransmitter biosynthetic genes. J. Neurosci. 15:8109–8120; 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilodeau, M.L., Boulineau, T., Greulich, J.D.M. et al. Differential expression of sympathoadrenal lineage-determining genes and phenotypic markers in cultured primary neural crest cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 37, 185–192 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2001)037<0185:DEOSLD>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2001)037<0185:DEOSLD>2.0.CO;2